Red eye, a common ocular condition, can be both alarming and uncomfortable. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for red eye, providing a detailed guide for individuals seeking to understand and manage this condition effectively.
Causes of Red Eye
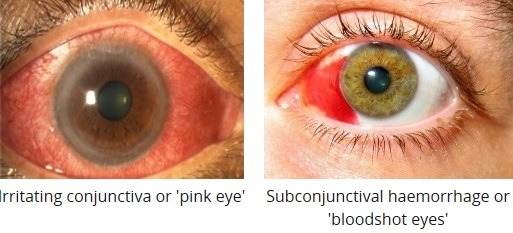
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin layer covering the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids. It can be caused by:
- Viruses: Commonly associated with colds, viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious.
- Bacteria: Often resulting from poor hygiene or contact lens misuse.
- Allergens: Pollen, dust, and pet dander can trigger allergic conjunctivitis.
- Irritants: Smoke, chemicals, and environmental pollutants.
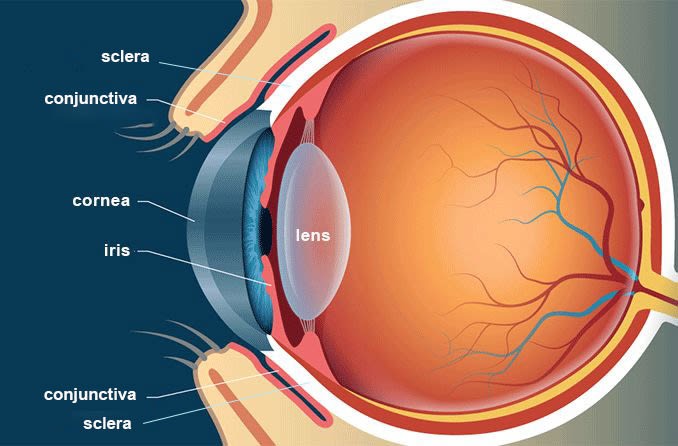
Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. Factors include:
- Aging: Tear production decreases with age.
- Environmental Conditions: Wind, smoke, and dry climates can exacerbate symptoms.
- Prolonged Screen Use: Staring at screens reduces blinking, leading to dry eyes.
Uveitis
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. Causes include:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Such as rheumatoid arthritis and sarcoidosis.
- Infections: Including herpes, tuberculosis, and syphilis.
- Injury: Trauma to the eye can trigger uveitis.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to high intraocular pressure. Symptoms can include red eye, severe headache, nausea, and blurred vision. Types of glaucoma:
- Open-Angle Glaucoma: The most common form, progresses slowly.
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: A medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
MUST READ: What Is Commonly Misdiagnosed as Pink Eye? 8 Issues Mistaken for Conjunctivitis
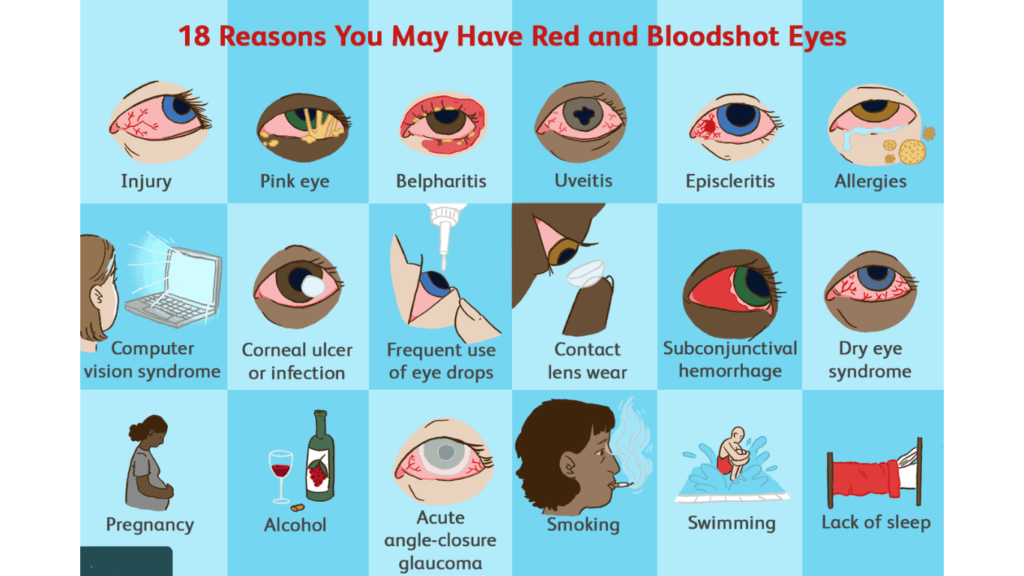
Symptoms of Red Eye
Common Symptoms
- Redness: Due to inflamed blood vessels.
- Itching: Often associated with allergic reactions.
- Burning Sensation: Common in dry eye syndrome.
- Discharge: Watery, mucous, or pus-like, depending on the cause.
- Swelling: Eyelids and conjunctiva may become swollen.
- Sensitivity to Light: Photophobia, especially in uveitis and glaucoma.
Diagnosis
Medical History
A thorough medical history helps identify potential causes, including recent infections, allergies, and contact lens use.
Physical Examination
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures how well you see at various distances.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: A microscope with a light to examine the eye in detail.
- Tonometry: Measures intraocular pressure, crucial for diagnosing glaucoma.
Laboratory Tests
- Cultures: For bacterial or viral infections.
- Blood Tests: To identify systemic conditions like autoimmune diseases.
- Allergy Testing: To pinpoint specific allergens.
Treatment Options
Home Remedies
- Cold Compresses: Reduce swelling and provide relief.
- Artificial Tears: Lubricate dry eyes.
- Avoid Allergens: Minimize exposure to known triggers.
Medications
- Antibiotic Drops/Ointments: For bacterial infections.
- Antiviral Medications: For viral infections like herpes.
- Antihistamines: For allergic conjunctivitis.
- Steroid Drops: For severe inflammation, under medical supervision.
Surgical Procedures
- Laser Surgery: For glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Vitrectomy: For severe cases of uveitis affecting the vitreous humor.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Hygiene Practices: Regular handwashing and avoiding touching the eyes.
- Proper Contact Lens Care: Adhering to cleaning and replacement schedules.
- Limiting Screen Time: Taking breaks to reduce eye strain.
Prevention
Regular Eye Exams
Routine eye exams help detect issues early and maintain overall eye health.
Protective Eyewear
Wearing safety glasses during activities that pose a risk to the eyes.
Manage Chronic Conditions
Effectively managing underlying health conditions to prevent ocular complications.
Healthy Diet
Consuming a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins A, C, and E to support eye health.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and symptoms of red eye is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. By following the outlined diagnostic procedures and treatment options, individuals can manage this condition and maintain optimal eye health. Regular check-ups and lifestyle adjustments play a significant role in preventing red eye and ensuring overall well-being.
