Eczema is a term that’s often thrown around in conversations about skin conditions, but not everyone knows there are different types. One less discussed type is papular eczema, which isn’t quite as “popular” in everyday discourse but is nonetheless significant. Papular eczema is a specific form of eczema characterized by small, raised bumps on the skin. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing it effectively and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Eczema
General Definition of Eczema
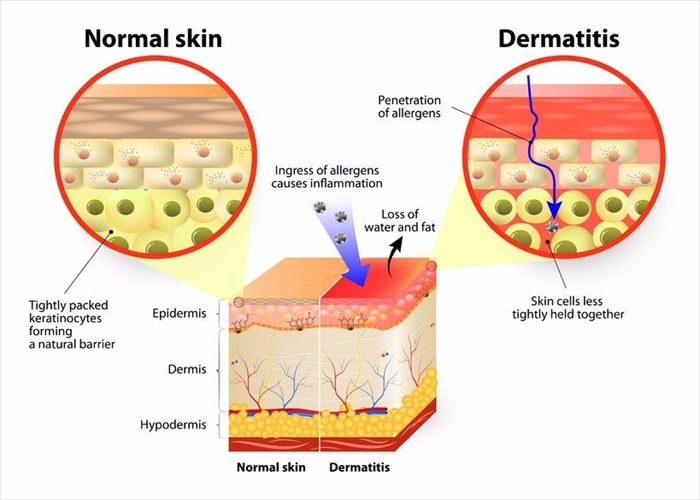
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, refers to a group of conditions that cause inflammation, itching, and redness of the skin. It’s a chronic problem for many and can be triggered by a variety of factors.
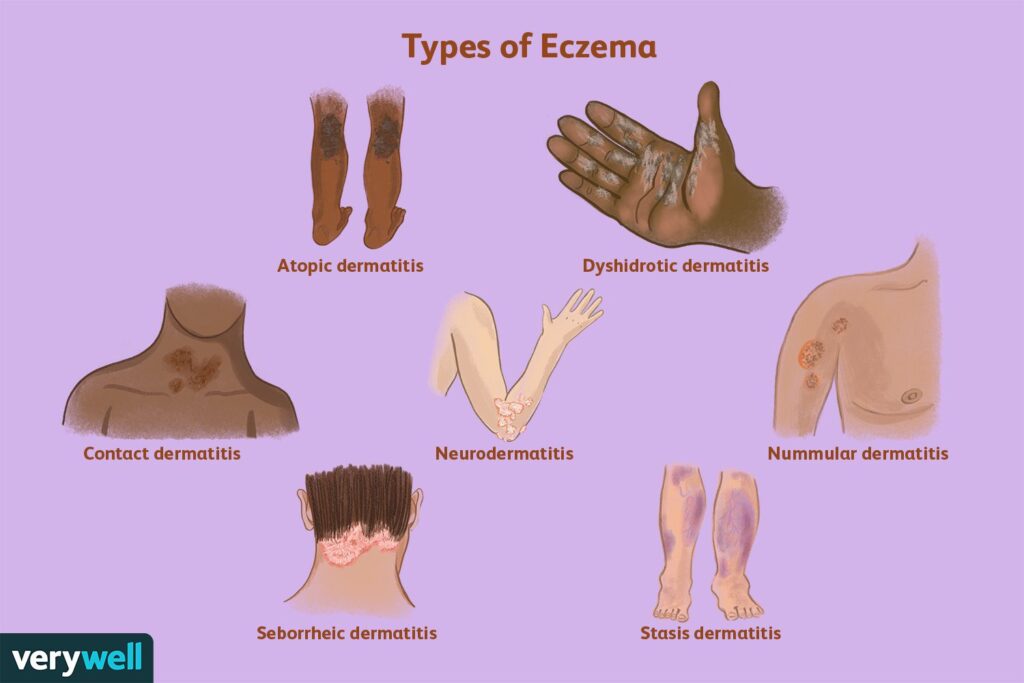
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, including:
- Atopic dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Nummular eczema
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Stasis dermatitis
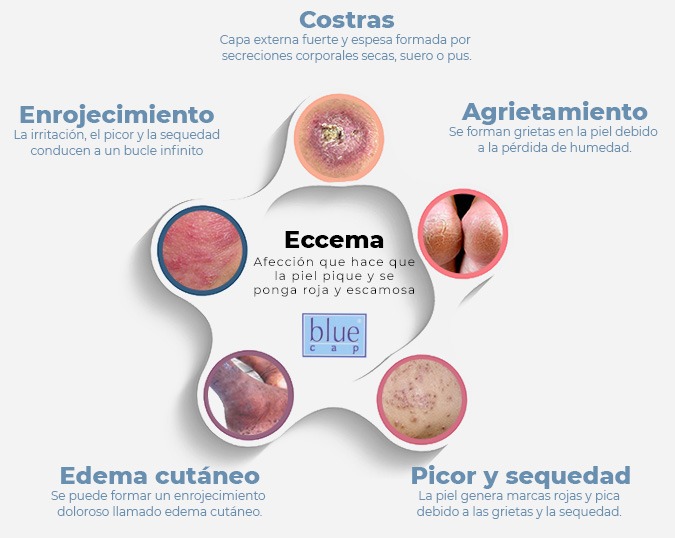
Common Symptoms of Eczema
Common symptoms include:
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Crusting
- Scaling
What is Papular Eczema?
Definition of Papular Eczema
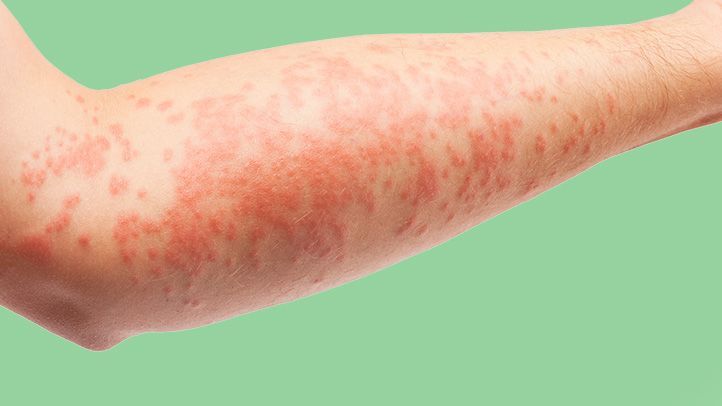
Bumpy Eczema, also known as lichenified eczema, is a chronic skin condition where small, firm bumps (papules) appear on the skin. These bumps can be extremely itchy and often lead to scratching, which exacerbates the condition.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of papular eczema include:
- Small, raised bumps on the skin
- Intense itching
- Redness and inflammation around the bumps
- Thickened, leathery patches of skin over time
Difference Between Papular Eczema and Other Types
Unlike atopic dermatitis, which can cause widespread red and inflamed patches, bumpy eczema is characterized by these distinct, small bumps. It’s crucial to differentiate between the two for proper treatment.
How to Identify Papular Eczema
Identifying papular eczema involves looking for clusters of small, itchy bumps. These are often more concentrated in specific areas rather than spread out.
Causes of Papular Eczema
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in the likelihood of developing papular eczema. If there is a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever, the chances of developing papular eczema increase.
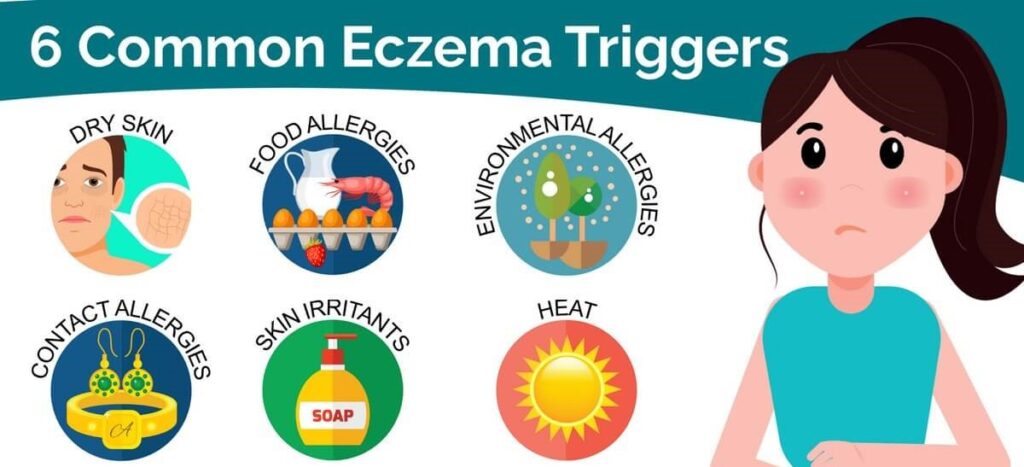
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors such as allergens, irritants, and climate can trigger or worsen papular eczema. Common triggers include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain fabrics.
Immune System Responses
An overactive immune system can also contribute to papular eczema. When the immune system mistakenly attacks the skin, it leads to inflammation and characteristic bumps.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying Symptoms of Papular Eczema
Identifying papular eczema involves recognizing its key symptoms, including the presence of small, itchy bumps, often grouped, and potential areas of thickened skin.
How It’s Diagnosed by Professionals
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough skin examination by a dermatologist. They may also take a patient history and perform skin tests to rule out other conditions.
Common Misdiagnoses
Papular eczema can be mistaken for other skin conditions like psoriasis or folliculitis due to the similarity in appearance. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
Impact on Daily Life
Physical Discomfort
The itching and discomfort caused by papular eczema can interfere with daily activities and sleep, leading to a significant decrease in quality of life.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Living with a chronic skin condition can take a toll on mental health. Feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and anxiety are common among those with papular eczema.
Social Implications
Visible skin conditions can affect social interactions and self-esteem. Many people with papular eczema may feel self-conscious about their appearance.
Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Mild cases of papular eczema can often be managed with over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams and antihistamines to reduce itching.
Prescription Medications
For more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe stronger topical steroids, immunomodulators, or even oral medications to control inflammation.
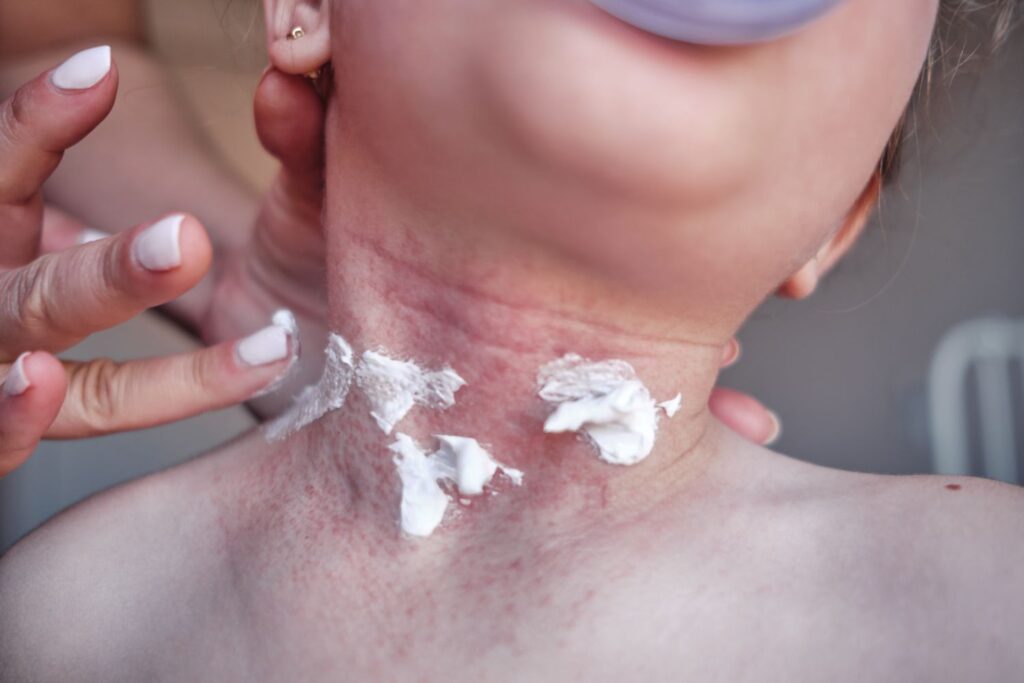
Natural and Home Remedies
Herbal Treatments
Herbal treatments such as chamomile, calendula, and aloe vera can soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
Dietary Changes
Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids can help manage symptoms.
Home Care Tips
Simple home care tips include using gentle soaps, taking lukewarm baths, and keeping the skin moisturized.
Preventative Measures
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage and prevent flare-ups. This includes avoiding known triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, and managing stress.
Skincare Routines
A proper skincare routine is crucial. This involves using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and reduce irritation.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is key. This can include certain foods, fabrics, or environmental factors like smoke or pollution.
Diet and Nutrition
Foods That May Trigger or Alleviate Symptoms
Some foods can trigger eczema flare-ups. Common culprits include dairy, gluten, and certain nuts. Conversely, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and flaxseeds, may help reduce inflammation.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall skin health and can help manage symptoms.
Supplements That May Help
Supplements like vitamin D, probiotics, and fish oil have shown promise in managing eczema symptoms, though they should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Living with Papular Eczema
Managing Flare-Ups
Managing flare-ups involves prompt treatment, avoiding scratching, and keeping the skin moisturized. Cold compresses can also help soothe itching.
Coping Strategies
Coping strategies might include mindfulness practices, joining support groups, and seeking therapy to manage the emotional impact of the condition.
Support Systems and Communities
Finding support from others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly beneficial. Online forums and local support groups offer a sense of community and shared experiences.
Papular Eczema in Children
Symptoms in Young Children
Children with bumpy eczema often show symptoms like small, itchy bumps, especially on the face, scalp, and limbs. These can be particularly distressing for young children.
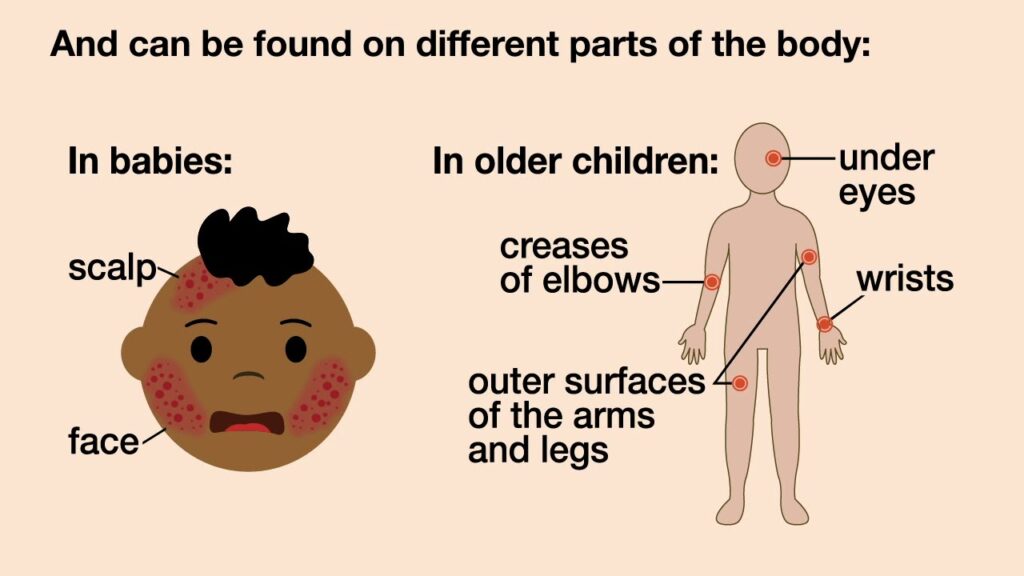
Special Considerations for Treatment
Treating eczema in children requires gentle, age-appropriate medications and a lot of patience. Parents need to ensure their child’s environment is as trigger-free as possible.
Supporting Children with Eczema
Supporting a child with eczema involves regular application of prescribed treatments, providing comfort during flare-ups, and educating the child on avoiding triggers.
Papular Dermatitis in Adults
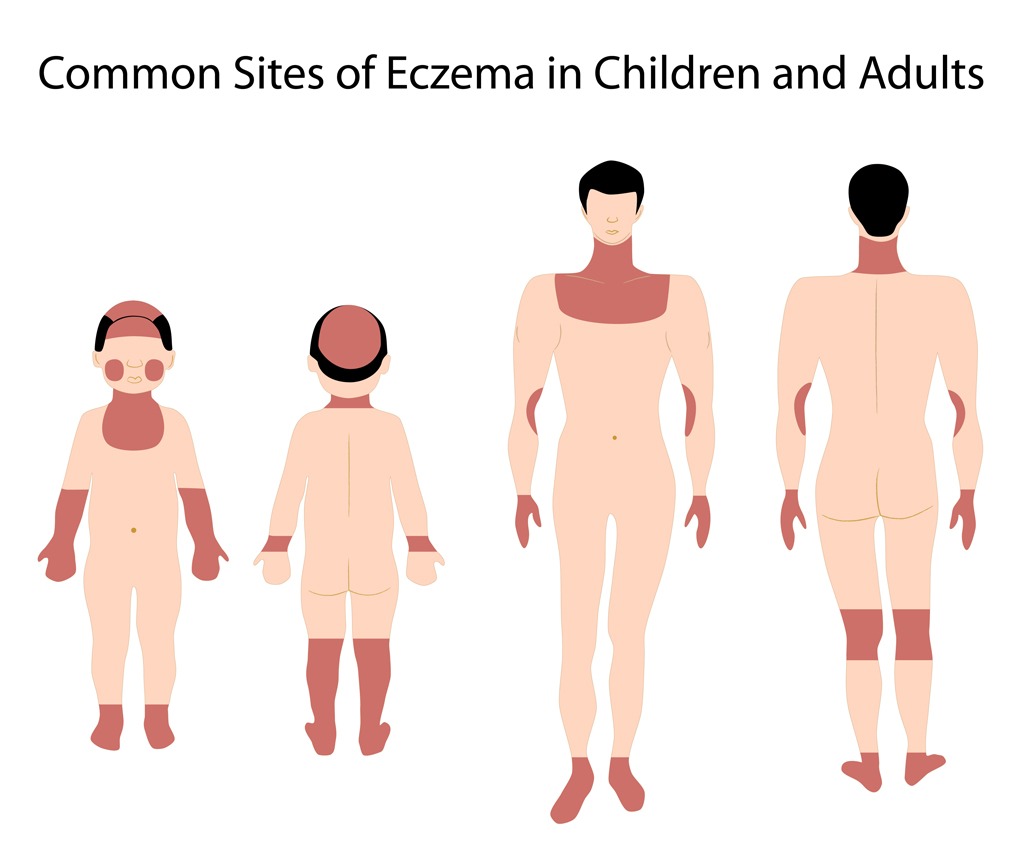
Differences in Symptoms from Children
In adults, papular eczema can appear on different parts of the body and may be more persistent. The skin may also become thicker and more leathery over time.
Adult-Specific Treatments
Adults may benefit from stronger treatments, including more potent topical steroids or systemic medications that target the immune system.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management involves ongoing skincare, avoiding triggers, and possibly making dietary changes. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial.
Papular Eczema and Mental Health
Psychological Impact
Living with papular dermatitis can take a toll on mental health, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression.
Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms include seeking therapy, joining support groups, and practicing stress-relief techniques like yoga and meditation.
Research and Future Directions
Current Research on Papular Eczema
Ongoing research aims to better understand the underlying causes of papular eczema and develop more effective treatments. Studies on the genetic and environmental factors are particularly promising.
Potential Future Treatments
Potential future treatments include biologics, which are targeted therapies that can more precisely modulate the immune system. These are already showing promise in clinical trials.
Clinical Trials and Studies
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge on papular eczema.
Myths and Misconceptions
Common Myths About Papular Dermatitis
There are many myths about eczema, such as it being contagious or purely a result of poor hygiene. It’s important to debunk these to reduce stigma.
Debunking Misinformation
Educating people about the realities of Bumpy eczema helps combat misinformation. Accurate information is key to understanding and managing the condition effectively.
Educating the Public
Public education campaigns and resources can help spread awareness about papular eczema, reducing stigma and promoting empathy.
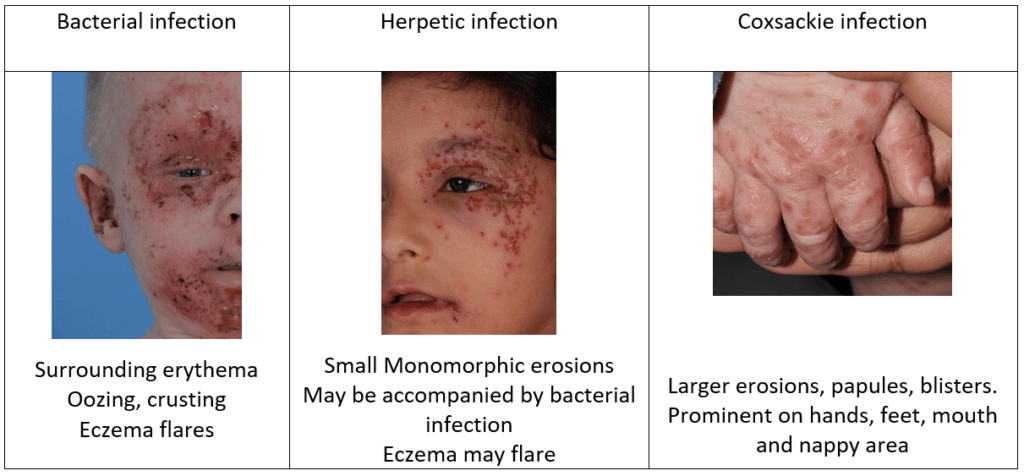
Case Studies
Real-Life Experiences of People with Bumpy Eczema
Hearing from people who live with papular eczema can provide valuable insights and highlight the diverse ways people manage the condition.
Treatment Successes and Challenges
Case studies often reveal that treatment is not one-size-fits-all. Successes and challenges vary, underscoring the importance of personalized care.
Lessons Learned
Lessons from these experiences can guide others in their journey with Bumpy eczema, offering practical advice and hope.
The Takeaway
In conclusion, papular eczema is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to manage effectively. Awareness, proper treatment, and support are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected. Educating ourselves and others can foster a more understanding and supportive environment for people with this condition.
