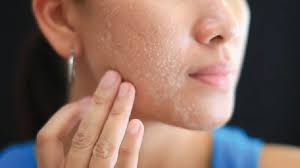
Dry skin is a common concern that many individuals grapple with, leading to discomfort and a desire for effective solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various aspects of dry skin, exploring its types, symptoms, causes, and practical tips for alleviating this condition.
1. Types of Dry Skin
Dry skin can manifest in various ways, often leaving individuals frustrated and seeking relief. To effectively address this concern, it’s crucial to understand the types of thirsty skin that one may encounter.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic condition causing inflamed and itchy skin. Individuals with this type of dry skin may experience flare-ups triggered by allergens or environmental factors.
Xerosis
Xerosis refers to generalized dry skin, often associated with inadequate hydration. Factors like harsh weather conditions or excessive bathing without moisturizing can contribute to xerosis.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This type of dry skin occurs when the skin reacts to a substance, leading to irritation and dryness. Identifying and avoiding the allergen is crucial for managing allergic contact dermatitis.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects oily areas of the skin, leading to redness and scaling. It commonly occurs on the scalp but can also affect other areas like the face and chest.
2. Symptoms and Causes
Itchy Sensation
One prevalent symptom of dry skin is persistent itching. This uncomfortable sensation often results from a lack of moisture in the skin, prompting individuals to scratch and exacerbate the dryness.
Flaky or Peeling Skin
Dry skin can manifest as flakiness or peeling, especially in areas prone to moisture loss. This occurs when the skin’s natural barrier is compromised, leading to visible signs of dehydration.
Redness and Irritation
Inflammation, redness, and irritation are common indicators of dry skin. Exposure to harsh environmental elements or allergens can exacerbate these symptoms.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes, can contribute to dry skin. Managing these underlying health issues is essential for effective thirsty skin care.
3. Why is My Skin So Dry?
Environmental Factors
Harsh weather conditions, low humidity levels, and exposure to extreme temperatures can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness. Protective measures like wearing appropriate clothing can mitigate these effects.
Harsh Cleansing Habits
Frequent use of harsh soaps or long, hot showers can disrupt the skin’s lipid barrier, contributing to dryness. Opting for mild cleansers and shorter, lukewarm showers can help maintain skin health.
Age-related Factors
As individuals age, the skin’s ability to retain moisture diminishes. Incorporating anti-aging skincare products and practices can help combat the effects of aging on skin hydration.
4. Where on My Body Will I Have Dehydrated Skin?
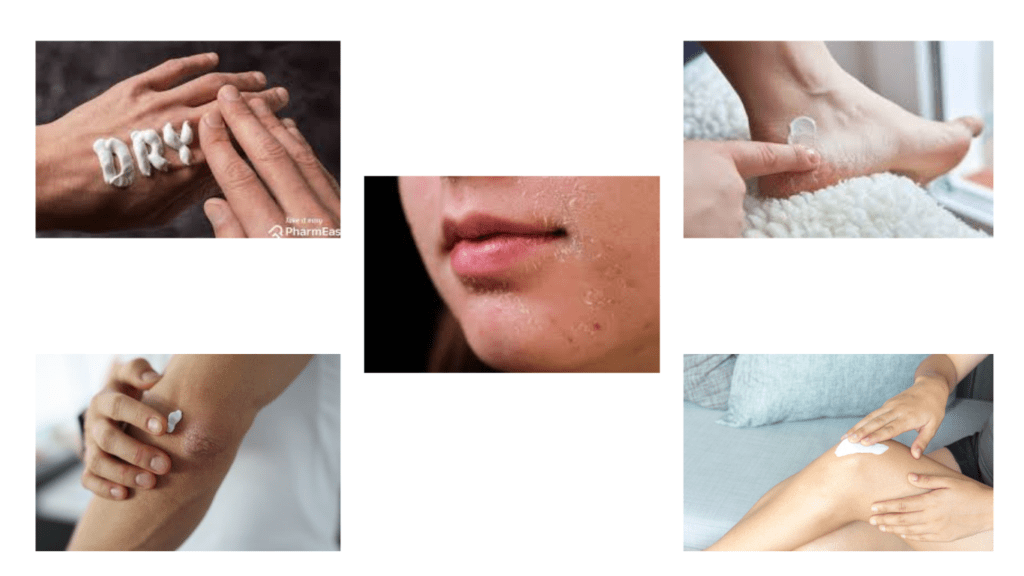
Facial Dryness
Facial skin is particularly prone to dryness due to its exposure to environmental elements and frequent facial expressions. Using a hydrating moisturizer and gentle cleanser can help maintain facial skin health.
Hands and Feet
The skin on the hands and feet is susceptible to dryness, especially during colder seasons. Regular moisturization and wearing gloves or socks can protect these areas from moisture loss.
Elbows and Knees
The joints, such as elbows and knees, often experience dryness due to friction and less oil production. Regular exfoliation and targeted moisturization can alleviate dryness in these areas.
5. How Do I Know If I Have Dry Skin?
The Touch Test
Gently touching your skin can reveal its moisture levels. Dry skin may feel rough, tight, or even exhibit visible flakiness upon touch.
Visual Inspection
Examining your skin visually can help identify dryness. Look for signs like redness, flakiness, or peeling, especially in areas prone to Dehydrated skin.
Persistent Itchiness
If you find yourself consistently itching, it may indicate dry skin. Addressing the underlying cause and adopting a moisturizing routine can alleviate this discomfort.
Unveiling the Tape Test
Diagnosing dry skin involves a simple test. Press a piece of transparent tape against your forehead, cheek, or any suspected dry area. If the tape pulls away easily and you notice flakes or scales, it’s likely dull skin.
6. Skincare Routine for Dry Skin with Tips

Gentle Cleansing
Opt for mild, hydrating cleansers that won’t strip the skin of its natural oils. Cleansing once or twice a day is sufficient to maintain skin cleanliness.
Hydrating Moisturizers
Choose moisturizers containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid and glycerin. Applying moisturizer immediately after bathing helps lock in moisture.
Exfoliation Techniques
Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells, promoting the absorption of moisturizers. Use a gentle exfoliant 1-2 times a week to maintain skin smoothness.
Incorporating Humidifiers
Using humidifiers in dry environments helps add moisture to the air, preventing skin from drying out. Place humidifiers in bedrooms or frequently used spaces for optimal results.
7. Suitable SPF in Moisturizers, Face Wash, and Beauty Products for Cracked Skin
SPF in Moisturizers
Opt for moisturizers with built-in at least SPF 30 to provide sun protection. This safeguards the skin from UV damage, a common contributor to dryness.
Face Wash Recommendations
Choose a gentle, hydrating face wash to cleanse without stripping away essential oils. Avoid products with harsh chemicals that can exacerbate Cracked skin.
Choosing Beauty Products Wisely
Select beauty products designed for cracky skin, including foundations and powders with moisturizing properties. Reading product labels can help identify suitable options.
8. How Can I Get Rid of Dry Skin?
Adequate Hydration
Staying well-hydrated from within is essential for maintaining skin moisture. Drink an ample amount of water throughout the day to support overall skin health.
Nutrient-rich Diet
Incorporate foods rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants into your diet. These nutrients contribute to skin health and combat dryness from the inside out.
Avoiding Long, Hot Showers
Limiting shower duration and using lukewarm water prevents excessive moisture loss. Patting the skin dry and applying moisturizer immediately afterward seals in hydration.
Natural Remedies
Explore natural remedies like coconut oil, aloe vera, or oatmeal-based products. These can offer soothing relief and enhance the skin’s natural moisture balance.
Closing
In conclusion, understanding and addressing Dehydrated skin requires a multifaceted approach. By recognizing the types, symptoms, and causes, individuals can tailor their skincare routines to effectively combat dryness. Implementing gentle cleansing habits, choosing suitable SPF products, and incorporating natural remedies can contribute to healthier, more hydrated skin.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Can dry skin be a sign of an underlying health condition?
- Yes, certain health conditions like hypothyroidism or diabetes can contribute to dry skin. Consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
- How often should I moisturize Cracked skin?
- It’s recommended to moisturize dry skin at least twice a day, particularly after bathing, to lock in moisture.
- Are there specific foods that can help combat dehydrated skin?
- Foods rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants, such as salmon, avocados, and berries, can promote skin health and combat dryness.
- Can I use natural remedies alongside commercial skincare products?
- Yes, natural remedies like coconut oil or aloe vera can complement commercial skincare products. However, it’s advisable to patch-test new ingredients to avoid potential allergies.
- Is dry skin more common in certain age groups?
- While dry skin can affect individuals of all ages, it tends to be more prevalent in older adults due to decreased skin moisture retention with age.