Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects how your body uses glucose, the main source of energy. In addition, Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. There are primarily two types of Sugar disease: type 1 and type 2.
Understanding the Root Causes of Diabetes
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to developing diabetes. If one or both parents have Sugar disease, there’s an increased likelihood of inheriting the condition.
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of diabetes.
Obesity and Lack of Physical Activity
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes
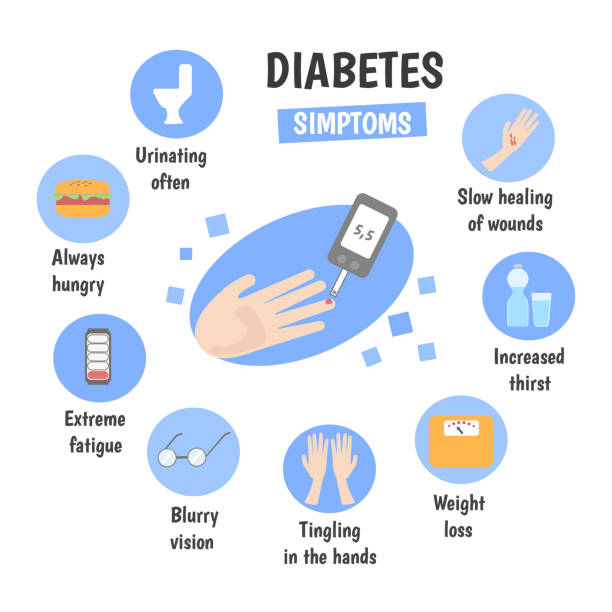
Common Symptoms
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow wound healing
- Unexplained weight loss
Early Signs to Watch Out For
It’s crucial to be vigilant about early signs of Glucose disorder, such as frequent urination, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like increased thirst and fatigue.
Managing Diabetes: Dietary Recommendations and Self-Care Strategies
Dietary Recommendations for Diabetic Patients
Foods to Include
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats

Foods to Avoid
- Sugary beverages
- Processed foods
- Foods high in saturated and trans fats
Self-Care Strategies for Diabetes Management
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes overall well-being.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels allows diabetic patients to track their progress and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plans.
Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into daily routines.
Medical Treatments for Glucose Disorder
Oral Medications
For type 2 Glucose disorder, oral medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones are commonly prescribed to help lower blood sugar levels.
Insulin Therapy
Type 1 diabetes and some cases of type 2 diabetes require insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Other Treatment Options
In addition to medications and insulin therapy, other treatment options such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and bariatric surgery may be recommended in certain cases.
Understanding the Dangerous Effects of Sugar Disease
Sugar disease can lead to various complications that affect multiple organ systems in the body.
Cardiovascular Complications
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease

Nerve Damage
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Charcot’s joint
Kidney Disease
Diabetic nephropathy is a common complication of Sugar disease, leading to kidney damage and potential kidney failure if left untreated.
Eye Problems
Diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts are common eye conditions associated with Sugar disease that can lead to vision impairment or blindness if not managed properly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes is a serious health condition that requires careful management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. By understanding the root causes, recognizing symptoms, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and following medical treatment recommendations, individuals with Glucose disorder can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
