Laser welding technology has revolutionized various industries with its precision, speed, and versatility. From automotive manufacturing to medical device production, a laser welder is an essential tool for creating strong, clean welds in a variety of materials.
Laser welding is a precise and efficient method used in various industries for joining metal parts. Unlike traditional welding techniques that rely on heat generated by electric arcs or flames, laser welding uses a concentrated beam of light to melt and fuse materials. This technology has revolutionized manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, speed, and versatility.
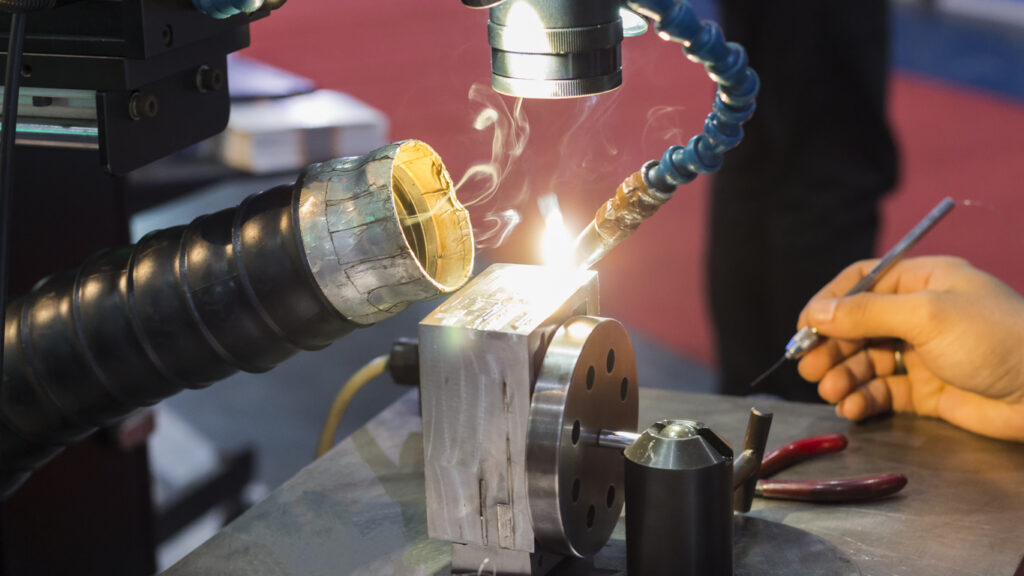

What Does a Laser Welder Do?
At its core, a laser welder emits a focused laser beam that heats and melts the material at the weld joint. The melted materials coalesce and solidify upon cooling, forming a strong and precise weld. Laser welders are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and electronics, where precision and cleanliness are critical.
Construction of a Laser Welder
A laser welder consists of several key components:
- Laser Source: Generates the laser beam, typically using gas, solid-state, or semiconductor technology.
- Beam Delivery System: Directs the laser beam to the weld joint, often through a series of mirrors and lenses.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating of the laser source and other components.
- Control System: Allows operators to adjust parameters such as beam intensity, focus, and duration.
The working mechanism involves generating a laser beam, focusing it on the workpiece, and controlling the movement and parameters to achieve the desired weld.
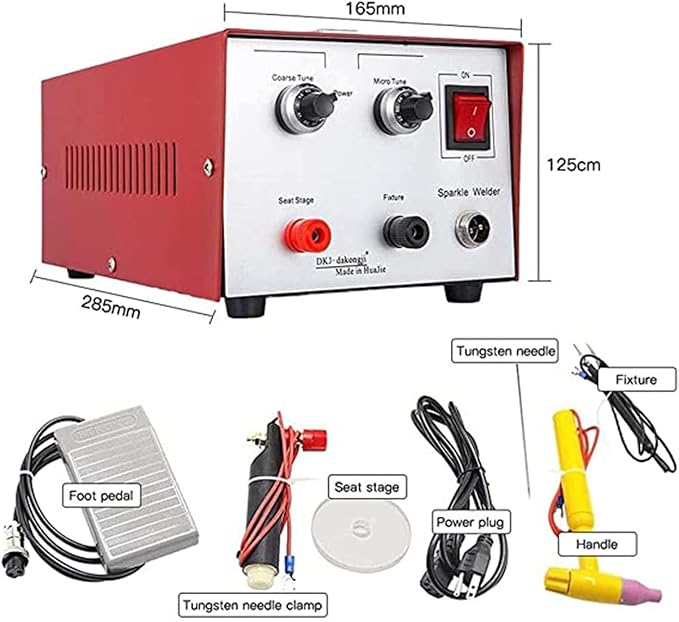

Types of Laser Welders
Laser welders come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
Gas Laser Welders
- CO2 Laser Welders: Use carbon dioxide gas to produce a high-power laser beam, ideal for cutting and welding thick materials.
Solid-State Laser Welders
- NdLaser Welders: Utilize a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet crystal as the lasing medium, suitable for precise and high-quality welds.
- Fiber Laser Welders: Use optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements, offering high efficiency and excellent beam quality.
Semiconductor Laser Welders
- These use semiconductor diodes to generate the laser beam, often used in micro-welding applications due to their compact size and precision.
Are Laser Welders Safe?
While laser welders are generally safe when used correctly, there are potential hazards. Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear, using appropriate ventilation, and following operational guidelines. Common hazards include exposure to intense light, fumes, and the risk of electrical shock.
Do Laser Welders Need Gas?
Yes, gas is often used in laser welding, but its role varies:
- Shielding Gas: Protects the weld pool from oxidation and contamination.
- Assist Gas: Helps in cutting and piercing applications by blowing away molten material.
Common Gases Used in Laser Welding
Common gases used in laser welding include:
- Argon: Provides excellent shielding and is widely used for welding various metals.
- Helium: Used for deep penetration welding due to its high thermal conductivity.
- Nitrogen: Sometimes used for stainless steel to prevent oxidation.
- Oxygen: Enhances cutting efficiency by reacting with the metal.
Each gas has its benefits, influencing the quality and characteristics of the weld.
Is Laser Welding the Future?
Advancements in laser welding technology, such as increased automation and improved beam quality, are paving the way for broader adoption. Industries are increasingly favoring laser welding for its precision, speed, and ability to weld complex geometries.
Which Welding is Strongest?
Laser welding offers some of the strongest welds due to its precision and control over the welding process. However, the strongest welding method depends on the application and materials used. Other methods like electron beam welding or traditional arc welding might be more suitable for specific tasks.
Is Laser Welding Difficult?
Laser welding requires a certain level of skill and understanding of the equipment and materials. Training and education are essential for operators to master the technique and achieve consistent, high-quality welds.
Which Metals Can Be Welded with a Laser Welder?
Laser welding is suitable for a wide range of metals, including:
- Steel: Both carbon steel and stainless steel.
- Aluminum: Requires precise control to prevent cracking.
- Titanium: Common in aerospace and medical industries for its strength and corrosion resistance.
- Nickel Alloys: Used in high-temperature applications.
- Copper: Used in electrical and electronic applications.
Each metal has specific considerations, such as laser power and welding speed, to ensure optimal results.

Advantages of Laser Welders
Precision
Laser welders offer unparalleled precision, making them ideal for applications where accuracy is critical.
Speed
Laser welding is a fast process, which increases productivity and reduces production time.
Quality
Laser welds are known for their high quality, with minimal distortion and a clean finish.
Versatility
Laser welders can be used on a wide range of materials and in various industries.
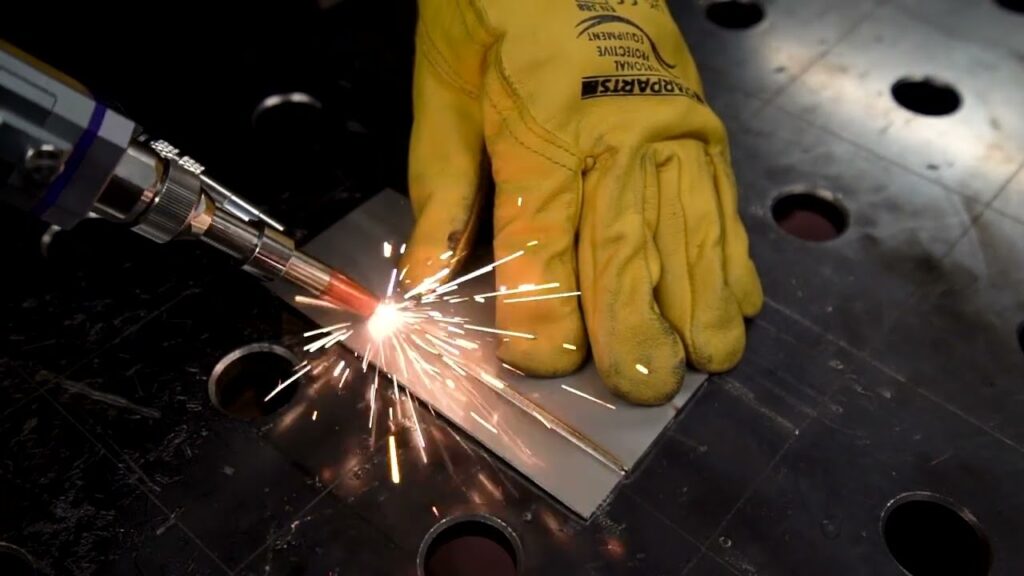

Disadvantages of Laser Welders
Cost
Laser welding equipment can be expensive, making the initial investment high.
Complexity
Requires specialized training and knowledge to operate effectively.
Maintenance
Laser welding systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Summary
Laser welding technology offers numerous benefits, including precision, speed, and high-quality welds. While it requires a significant investment and specialized training, the advantages it brings to various industries make it a valuable tool for the future of welding. As technology continues to advance, laser welding is likely to become even more prevalent, offering new possibilities and applications.
