If you’re looking for a comprehensive way to improve your liver health, the 21-day fatty liver diet plan is an excellent starting point. This plan focuses on dietary changes designed to help reduce liver fat and improve overall liver function. The liver is a crucial organ that plays many vital roles in the body, and maintaining its health is essential for overall well-being.
Understanding the Liver
Where is the liver located?
The liver is a large, reddish-brown organ located in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm and above your stomach. It’s the body’s largest internal organ and weighs about three pounds in adults.
Functions of the liver
The liver performs over 500 functions, including detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, storing vitamins and minerals, and regulating blood clotting. It also plays a vital role in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
What is NAFLD?
Definition and types of NAFLD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver cells in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. NAFLD can be classified into two main types:
- Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): Excess fat in the liver without significant inflammation or liver damage.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Fat accumulation accompanied by inflammation and liver cell damage, which can progress to fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) vs. alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD)
While NAFLD is caused by factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is directly related to excessive alcohol consumption. Both conditions can lead to serious liver damage if left untreated.
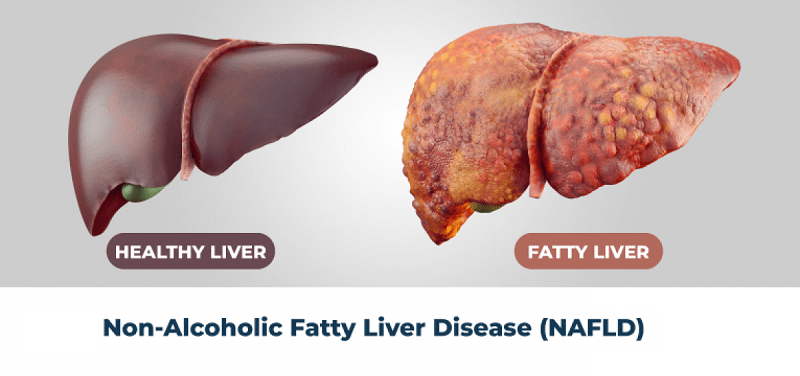
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Causes of NAFLD
NAFLD is primarily linked to metabolic risk factors like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol. A sedentary lifestyle and poor diet also contribute significantly to its development.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Often, NAFLD presents no symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose without medical testing. When symptoms do occur, they may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and an enlarged liver. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy.
Complications if untreated
If NAFLD progresses to NASH, it can cause liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Early intervention with lifestyle changes can prevent these severe outcomes.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
Causes of AFLD
AFLD results from heavy alcohol consumption, which impairs the liver’s ability to process fats. This leads to fat accumulation in liver cells.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of AFLD can include jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis is based on medical history, blood tests, and imaging studies.
Complications if untreated
Chronic AFLD can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake is crucial to managing and reversing AFLD.
Foods to Avoid for Fatty Liver Disease
Processed foods
Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats, sugars, and preservatives that can exacerbate liver fat accumulation.
Sugary beverages
Drinks high in sugar, like sodas and sweetened juices, contribute to liver fat and should be avoided.
Refined grains
Refined grains, such as white bread and pasta, have been stripped of their nutrients and can spike blood sugar levels, promoting fat storage.
High-fat dairy products
Full-fat milk, cheese, and yogurt can increase fat intake, which is harmful to a fatty liver.
Fried foods
Fried foods are high in unhealthy fats and calories, leading to weight gain and liver fat accumulation.
What You Cannot Eat with Fatty Liver
A diet for fatty liver disease should exclude:
- Sugary foods: Cakes, cookies, candies
- Refined carbohydrates: White bread, pastries
- High-fat dairy: Full-fat milk, cheese
- Red meat: Beef, pork, and lamb
- Fried and fast food: French fries, burgers
- Alcohol: All forms
What You Can Eat with Fatty Liver
Fruits and vegetables
Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these should form the cornerstone of your diet. Aim for a variety of colors to ensure a range of nutrients.
Whole grains
Brown rice, quinoa, and oats are excellent sources of fiber, which helps maintain a healthy weight and improve liver function.

Lean proteins
Opt for fish, skinless poultry, tofu, and legumes to reduce fat intake while providing essential nutrients.
Healthy fats
Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which help reduce liver fat.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Real-life stories of individuals who have successfully managed or reversed fatty liver disease can provide motivation and practical insights into the challenges and successes of adhering to a 21-day fatty liver diet plan.
Expert Insights
Medical professionals emphasize the importance of early intervention and consistent lifestyle changes in managing fatty liver disease. Regular check-ups and monitoring are crucial for preventing progression.
21-Day Fatty Liver Diet Plan: Weekly Breakdown
The 21-day fatty liver diet plan is divided into three phases to detoxify, nourish, and maintain liver health.

Day 1-7: Detox Phase
Focus on eliminating toxins and reducing inflammation.
i. Day 1-3: Hydration and Simple Foods
- Morning: Start with a glass of warm lemon water.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a sprinkle of flax seeds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with a variety of vegetables.
- Dinner: Steamed fish with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
- Snacks: Fresh fruits, nuts, and seeds.
ii. Day 4-7: Increasing Fiber and Nutrients
- Morning: Green smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk.
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with avocado and poached eggs.
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a side of mixed greens.
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables and brown rice.
- Snacks: Carrot sticks with hummus, apple slices with almond butter.
Day 8-14: Nutrient-Rich Phase
Introduce nutrient-dense foods to support liver repair.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and flaxseeds
- Lunch: Lentil soup with whole-grain bread
- Dinner: Grilled chicken with a side of quinoa and kale
- Snacks: Greek yogurt with honey, vegetable sticks with hummus
Day 15-21: Maintenance Phase
Continue with a balanced diet to sustain liver health.
- Breakfast: Smoothie bowl with mixed fruits and nuts
- Lunch: Turkey wrap with whole grain tortilla and plenty of veggies
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with brown rice and vegetables
- Snacks: Apple slices with almond butter, dark chocolate
Daily Breakdown
Here’s a detailed breakdown of sample meals for each phase of the 21-day fatty liver diet plan:
Day 1: Detox Phase
- Breakfast: Green smoothie with spinach, banana, and chia seeds
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables
- Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed broccoli
- Snacks: Fresh fruit, nuts
Day 2: Detox Phase
- Breakfast: Avocado toast on whole-grain bread
- Lunch: Vegetable soup with barley
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with a side of mixed greens
- Snacks: Carrot sticks with hummus, apple slices
Continue with similar meals, focusing on fresh, whole foods and avoiding processed items.

Recipes for the 21-Day Fatty Liver Diet Plan
Breakfast recipes
- Green Smoothie: Blend 1 cup spinach, 1 banana, 1 tablespoon chia seeds, and 1 cup almond milk.
- Oatmeal with Berries: Cook 1 cup oatmeal, top with 1/2 cup mixed berries and 1 tablespoon flaxseeds.
Lunch recipes
- Quinoa Salad: Mix 1 cup cooked quinoa, 1/2 cup cherry tomatoes, 1/2 cup cucumbers, and 1/4 cup feta cheese.
- Lentil Soup: Combine 1 cup lentils, 1 chopped carrot, 1 chopped celery stalk, and 4 cups vegetable broth. Simmer until tender.

Dinner Recipes
- Baked Salmon: Season 1 salmon fillet with lemon and herbs. Bake at 375°F for 20 minutes.
- Grilled Chicken: Marinate 1 chicken breast in olive oil and herbs, then grill until cooked through.
Snack recipes
- Greek Yogurt with Honey: Mix 1 cup Greek yogurt with 1 tablespoon of honey.
- Apple Slices with Almond Butter: Slice 1 apple and serve with 2 tablespoons of almond butter.
Tips for Sticking to the Diet
Meal prepping
Prepare meals in advance to ensure you have healthy options readily available, reducing the temptation to eat unhealthy foods.
Staying hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support liver function and overall health.
Mindful eating
Pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues, and eat slowly to help with digestion and avoid overeating.
Exercise and Lifestyle Changes
Importance of physical activity
Regular exercise helps reduce liver fat, improves metabolism, and supports overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Stress management techniques
Practice stress-relieving activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to help maintain liver health and overall well-being.
Monitoring Progress
Tracking symptoms
Keep a journal of your symptoms and dietary changes to monitor your progress and identify any foods that may trigger symptoms.
Regular medical check-ups
Visit your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your liver health and make any necessary adjustments to your diet or lifestyle.
summary
The 21-day fatty liver diet plan is a structured approach to improving liver health through dietary changes and lifestyle adjustments. By following this plan, you can help reduce liver fat, enhance liver function, and improve your overall health. Prioritizing your liver health today can lead to a healthier, happier future.
